InfiR2: A Comprehensive FP8 Training Recipe for Reasoning-Enhanced Language Models
Wenjun Wang*¹, Shuo Cai*¹, Congkai Xie², Mingfa Feng², Yiming Zhang¹, Zhen Li¹², Kejing Yang², Ming Li¹, Jiannong Cao¹, Hongxia Yang¹²
¹The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, ²InfiX.ai
Abstract
The immense computational cost of training Large Language Models (LLMs) presents a major barrier to innovation. While FP8 training offers a promising solution with significant theoretical efficiency gains, its widespread adoption has been hindered by the lack of a comprehensive, open-source training recipe. To bridge this gap, we introduce an end-to-end FP8 training recipe that seamlessly integrates continual pre-training and supervised fine-tuning. Our methodology employs a fine-grained, hybrid-granularity quantization strategy to maintain numerical fidelity while maximizing computational efficiency. Through extensive experiments, including the continue pre-training of models on a 160B-token corpus, we demonstrate that our recipe is not only remarkably stable but also essentially lossless, achieving performance on par with the BF16 baseline across a suite of reasoning benchmarks. Crucially, this is achieved with substantial efficiency improvements, including up to a 22% reduction in training time, a 14% decrease in peak memory usage, and a 19% increase in throughput. Our results establish FP8 as a practical and robust alternative to BF16, and we will release the accompanying code to further democratize large-scale model training.
Main Contributions
- End-to-End FP8 Training Recipe: InfiR2 is the first open-source, end-to-end FP8 training recipe that unifies continual pre-training and supervised fine-tuning in one workflow, offering a practical alternative to traditional BF16 training. It resolves the longstanding difficulties that prevented FP8 from being used in full model training pipelines.
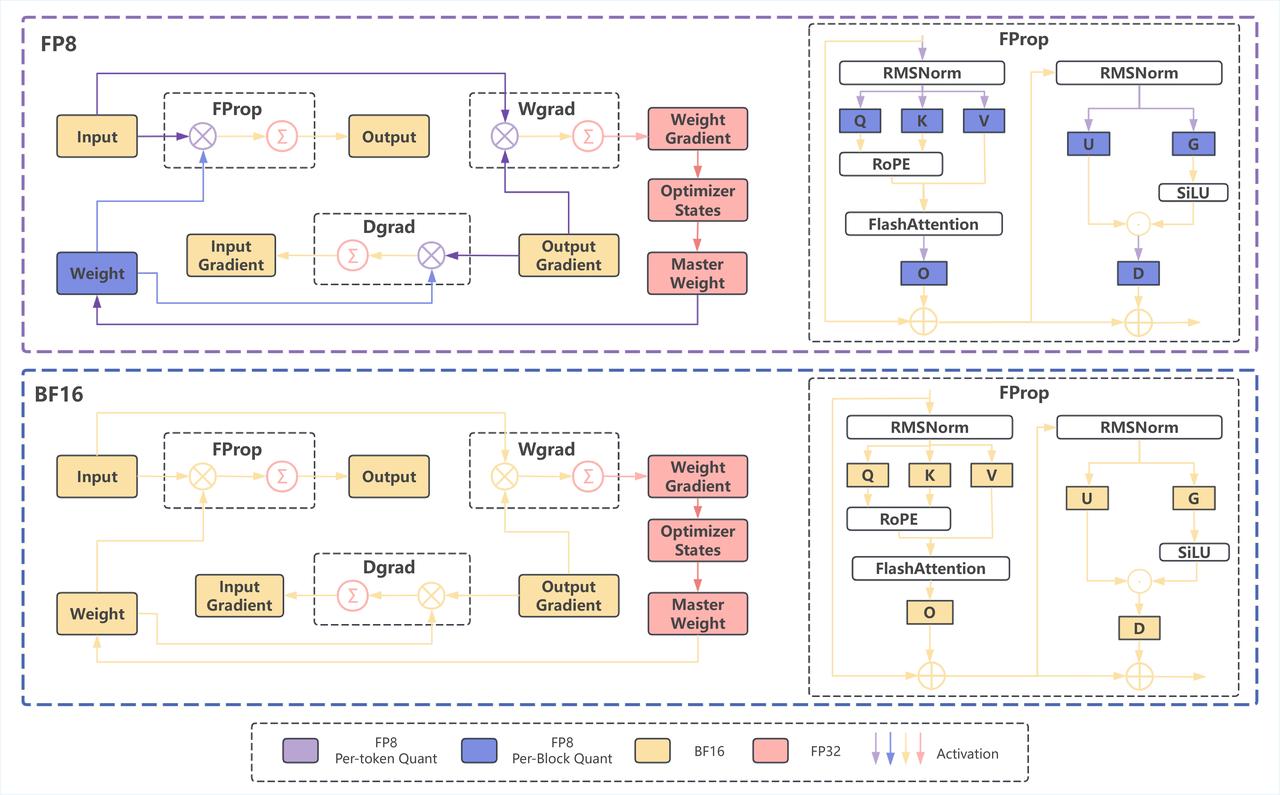
- Hybrid-Granularity Quantization: InfiR2 implements finer-grained FP8 quantization for computationally intensive operators, as shown in Figure 1: -For Linear/GEMM operations, it applies block-wise quantization to weights and token-wise quantization to activations. This balances accuracy with computational speed to fully leverage the hardware value of Tensor Cores. -For critical components like Master Weights, Optimizer States, and Gradient Accumulation, it employs a high-precision strategy for direct optimization and updates, effectively providing a "safety belt" for the most crucial parts of model training.
- Stable and Reproducible Performance: We demonstrate for the first time that FP8 training can match full-precision training in quality across critical reasoning benchmarks. InfiR2's FP8-trained models achieve accuracy on par with BF16 on tasks like AIME, GPQA, and LiveCodeBench (often within 1-2% or less). Notably, for smaller models (e.g. ~7B parameters), FP8 training even slightly outperforms BF16 on some benchmarks (acting as a form of regularization), confirming that FP8 is not only computationally lighter but also rock-solid in training convergence.
- Community Release & Impact: Based on this complete FP8 training workflow (applying CPT and SFT to the Qwen-2.5 model series), we have developed two high-performing models: InfiR2-1.5B-FP8 and InfiR2-7B-FP8. We are open-sourcing the model checkpoints and the complete training code repository to the community.
Pretraining performance comparison between FP8 and BF16.
Experiments
- Pretraining with FP8 is lossless. InfiR2-1.5B-FP8 shows almost no performance loss on AIME25, AIME24, GPQA, and LiveCodeBench compared to the BF16 baseline, as detailed in the results below.
| Base Model | Quantization Method | AIME 25 | AIME24 | GPQA | LiveCodeBench v5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2.5-Math-7B (Stage 1) | BF16 | 44.16 | 56.87 | 45.14 | 32.22 |
| FP8 w. FP32 scale | 44.06 | 56.67 | 47.98 | 32.18 | |
| FP8 | 44.89 | 57.81 | 47.10 | 31.34 | |
| Qwen2.5-Math-7B (Stage 2) | BF16 | 50.00 | 59.48 | 48.36 | 35.22 |
| FP8 w. FP32 scale | 46.46 | 57.92 | 45.39 | 35.87 | |
| FP8 | 49.79 | 59.69 | 46.78 | 36.21 | |
| Qwen2.5-Math-1.5B (Stage 1) | BF16 | 15.41 | 18.33 | 24.68 | 10.71 |
| FP8 w. FP32 scale | 15.73 | 18.65 | 25.38 | 10.14 | |
| FP8 | 17.50 | 16.88 | 23.17 | 9.84 | |
| Qwen2.5-Math-1.5B (Stage 2) | BF16 | 17.92 | 21.35 | 24.48 | 12.16 |
| FP8 w. FP32 scale | 20.62 | 22.81 | 27.78 | 12.69 | |
| FP8 | 20.73 | 21.77 | 25.13 | 12.96 |
- SFT with FP8 is lossless. After fine-tuning, Qwen2.5-Math-1.5B and 7B also show no degradation compared to the BF16 baseline, and even achieve a 1-2 point improvement on the AIME math competition dataset, as detailed in the results below.
| AIME 25 | AIME 24 | GPQA | LiveCodeBench v5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF16 | 17.91 | 17.50 | 31.94 | 16.41 |
| FP8 | 18.45 | 17.39 | 29.48 | 17.10 |
- Memory optimization and Speed up. Memory Optimization & Computation Acceleration: Compared to the widely used BF16, FP8 delivers: -Up to 22% increase in end-to-end training speed. -Up to 14% savings in peak memory usage. -Up to 19% increase in end-to-end throughput.
Model Size = 1.5B
Context Length = 32k, TP = 2, CP = 1, MBS = 1
| Forward | Backward | Total | Ratio | Peak Memory | Ratio | Throughput | Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF16 | 841 ms | 2329 ms | 3170 ms | - | 57.8 GB | - | 345 TFlops | - |
| FP8 | 875 ms | 2075 ms | 2950 ms | 0.93× | 51.7 GB | 0.89× | 360 TFlops | 1.04× |
Context Length = 8k, TP = 1, CP = 1, MBS = 2
| Forward | Backward | Total | Ratio | Peak Memory | Ratio | Throughput | Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF16 | 463 ms | 1567 ms | 2030 ms | - | 68.1 GB | - | 340 TFlops | - |
| FP8 | 529 ms | 1061 ms | 1590 ms | 0.78× | 58.3 GB | 0.86× | 376 TFlops | 1.10× |
Model Size = 7B
Context Length = 32k, TP = 4, CP = 1, MBS = 1
| Forward | Backward | Total | Ratio | Peak Memory | Ratio | Throughput | Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF16 | 2790 ms | 6800 ms | 9590 ms | - | 78.1 GB | - | 409 TFlops | - |
| FP8 | 2660 ms | 5700 ms | 8360 ms | 0.87× | 67.4 GB | 0.86× | 461 TFlops | 1.14× |
Context Length = 8k, TP = 2, CP = 1, MBS = 1
| Forward | Backward | Total | Ratio | Peak Memory | Ratio | Throughput | Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF16 | 1760 ms | 5320 ms | 7080 ms | - | 53.2 GB | - | 453 TFlops | - |
| FP8 | 2300 ms | 3230 ms | 5530 ms | 0.78× | 50.8 GB | 0.95× | 537 TFlops | 1.19× |
Citation Information
If you find this work useful, citations to the following papers are welcome:
@misc{wang2025infir2comprehensivefp8training,
title={InfiR2: A Comprehensive FP8 Training Recipe for Reasoning-Enhanced Language Models},
author={Wenjun Wang and Shuo Cai and Congkai Xie and Mingfa Feng and Yiming Zhang and Zhen Li and Kejing Yang and Ming Li and Jiannong Cao and Hongxia Yang},
year={2025},
eprint={2509.22536},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.22536},
}
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude for the following open-source projects: Slime, LLaMA-Factory, and Qwen2.5